Exception Handling
Exception Handling
Exception handling is a process in .NET that deals with unexpected or exceptional conditions that occur during the execution of a program. These conditions, also known as exceptions, can result from various circumstances, such as invalid user input, physical I/O errors, or logical errors in your program.
Try-Catch-Finally
The try-catch-finally construct is used to handle exceptions in C#.
- The
tryblock contains the code that may potentially generate an exception. - The
catchblock is where you catch and handle the exception if one occurs. - The
finallyblock is optional and contains code that is always executed, whether an exception occurs or not.
You can have multiple catch blocks to handle different types of exceptions. The CLR will execute the first catch block that can handle the exception thrown. If none of the catch blocks match, the exception will go unhandled.
Throwing Exceptions
You can throw exceptions using the throw keyword. Throwing an exception immediately transfers the control flow to the nearest relevant catch block.
throw new Exception("Something went wrong");
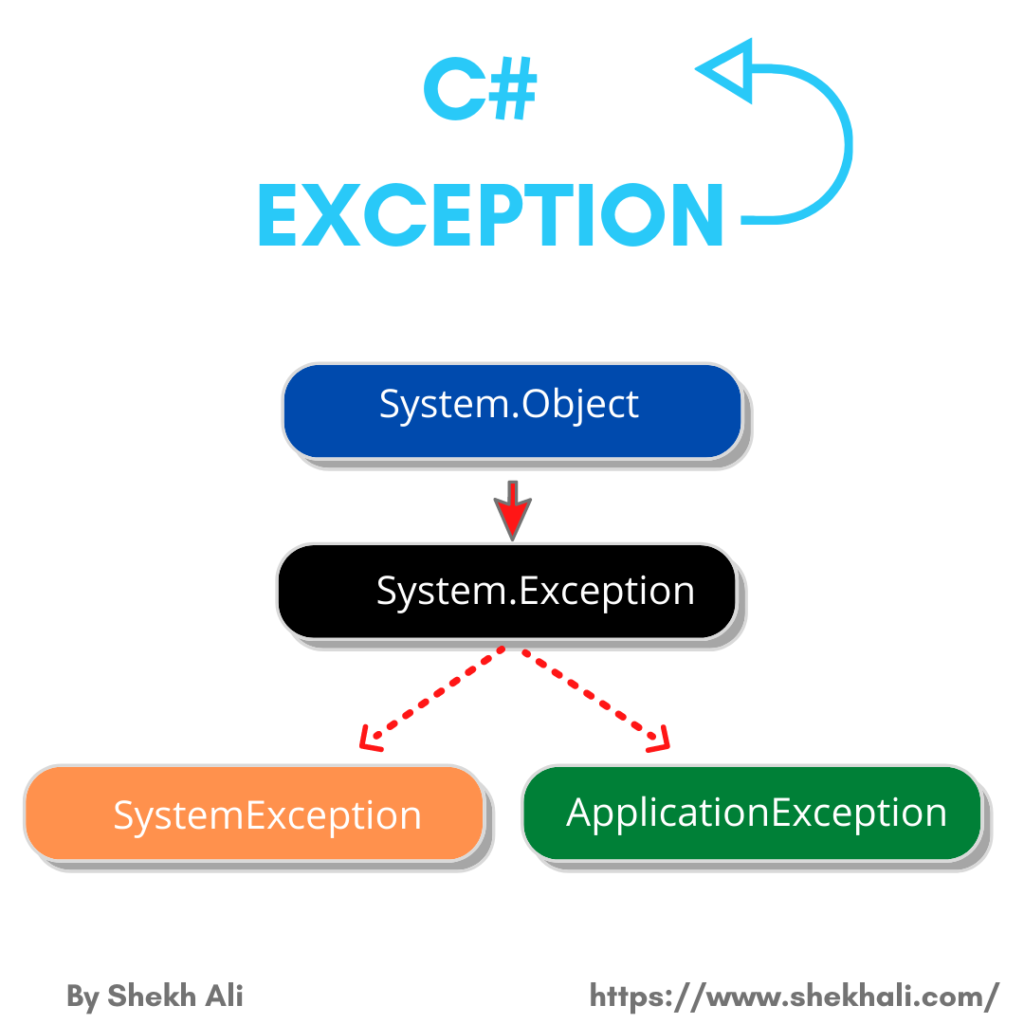
Exception Types
There are many types of exceptions in .NET, and you can create your own by deriving from the Exception class. Here are a few examples:
SystemException: A base class for all predefined system exception.IndexOutOfRangeException: Thrown when an attempt is made to access an element of an array with an index that is outside its bounds.ArgumentNullException: Thrown when a null reference is passed to a method that does not accept it as a valid argument.DivideByZeroException: Thrown when an attempt is made to divide an integral or decimal value by zero