.NET Package Management with NuGet and .NET Libraries
.NET Libraries
.NET Libraries are often distributed as packages that can be easily added to any project. Here are some of the most commonly used .NET libraries:
- System: The System namespace contains fundamental classes and base classes that define commonly used value and reference data types, events and event handlers, interfaces, attributes, and processing exceptions.
- System.IO: The System.IO namespace contains types that allow reading and writing to files and data streams, and types that provide basic file and directory support.
- System.Collections: The System.Collections namespace contains interfaces and classes that define various collections of objects, such as lists, queues, bit arrays, hash tables, and dictionaries.
- System.Linq: The System.Linq namespace provides classes and interfaces that support queries that use Language-Integrated Query (LINQ).
- System.Net: The System.Net namespace provides a simple programming interface for many of the protocols used on networks today.
- System.Threading: The System.Threading namespace provides classes and interfaces that enable multithreaded programming.
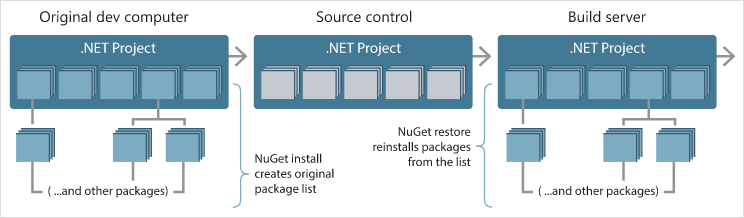
The primary tool for package management in .NET is NuGet.
What is NuGet?
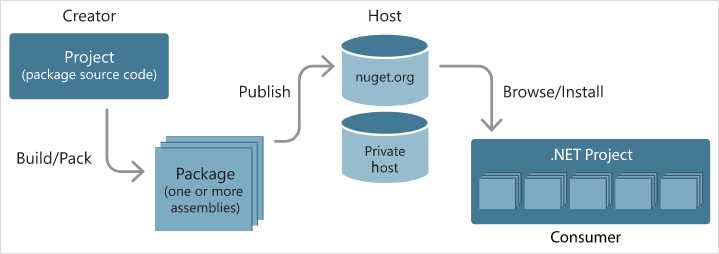
NuGet is a free and open-source package manager for the Microsoft development platform. It allows developers to share and consume useful code. A NuGet package is a single ZIP file with the .nupkg extension that contains compiled code (DLLs), other files related to that code, and a descriptive manifest that includes information like the package's version number.
Using NuGet
NuGet is integrated into Visual Studio, and you can use it through the Package Manager Console or the Manage NuGet Packages dialog box.
To install a package in Visual Studio:
- Right-click on the project and choose Manage NuGet Packages.
- In the dialog box that appears, choose the Browse tab and search for the package you need (e.g., Newtonsoft.Json).
- Click on the package in the list and click Install.
The package and its dependencies will be downloaded and added to your project, and you can start using the classes and methods it provides.